Malignités
Clinical Trials (Controlled Treatment Period)1,2
- During the clinical trials (controlled treatment period) of ocrelizumab in MS, malignancy was reported in 4 patients in the interferon-beta 1a/ placebo arms and 15 patients in the ocrelizumab arms. Of the 15 patients in the ocrelizumab arms:
- Breast cancer was reported in 6 female patients (there were no reports of breast cancer in the comparator arms)
- NMSC was reported in 4 patients
- The remaining 5 malignancies in patients treated with ocrelizumab were single cases: renal cancer, anaplastic large-cell cancer, pancreatic neoplasm, endometrial cancer, and malignant melanoma
Clinical Trials (Ocrelizumab All-Exposure Population)3
- As of January 2019, the age- and sex-standardised incidence rate of malignancies (excluding NMSC*) per 100 PY in the ocrelizumab all-exposure population (detailed in Figure 1 footnote) remained stable over time, with the confidence intervals overlapping and within epidemiological references (Figure 1A)
- The age-standardised incidence rate of female breast cancer remained stable over time, with the confidence intervals overlapping and within epidemiological references (Figure 1B)
- Yearly incidence rates of all malignancies and female breast cancer fluctuate and do not suggest a time-dependent exposure effect (Table 1)
Figure 1: Standardised Incidence Rates per 100 PY Over Time of All Malignancies (A) and Female Breast Cancer (B)a
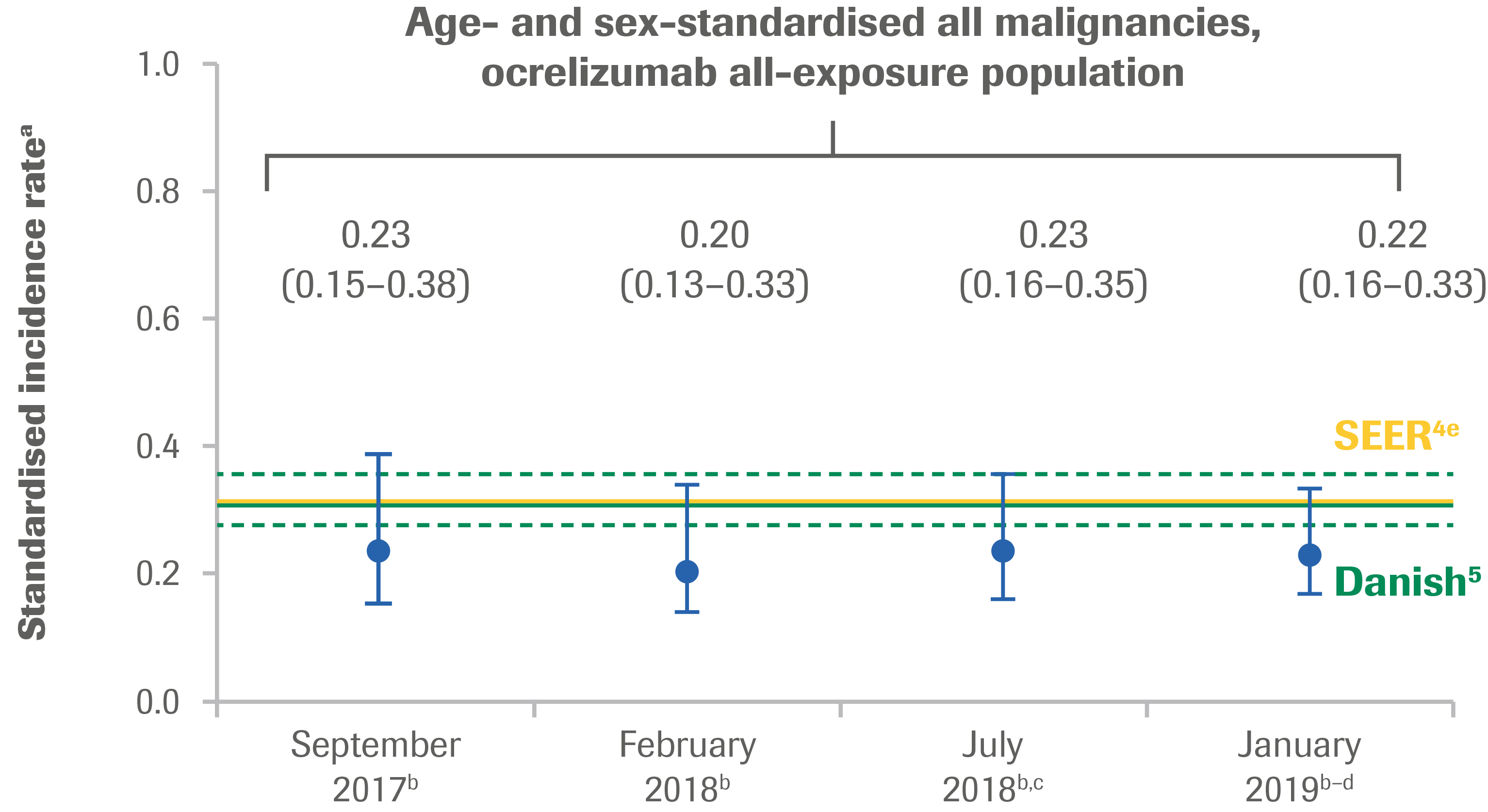
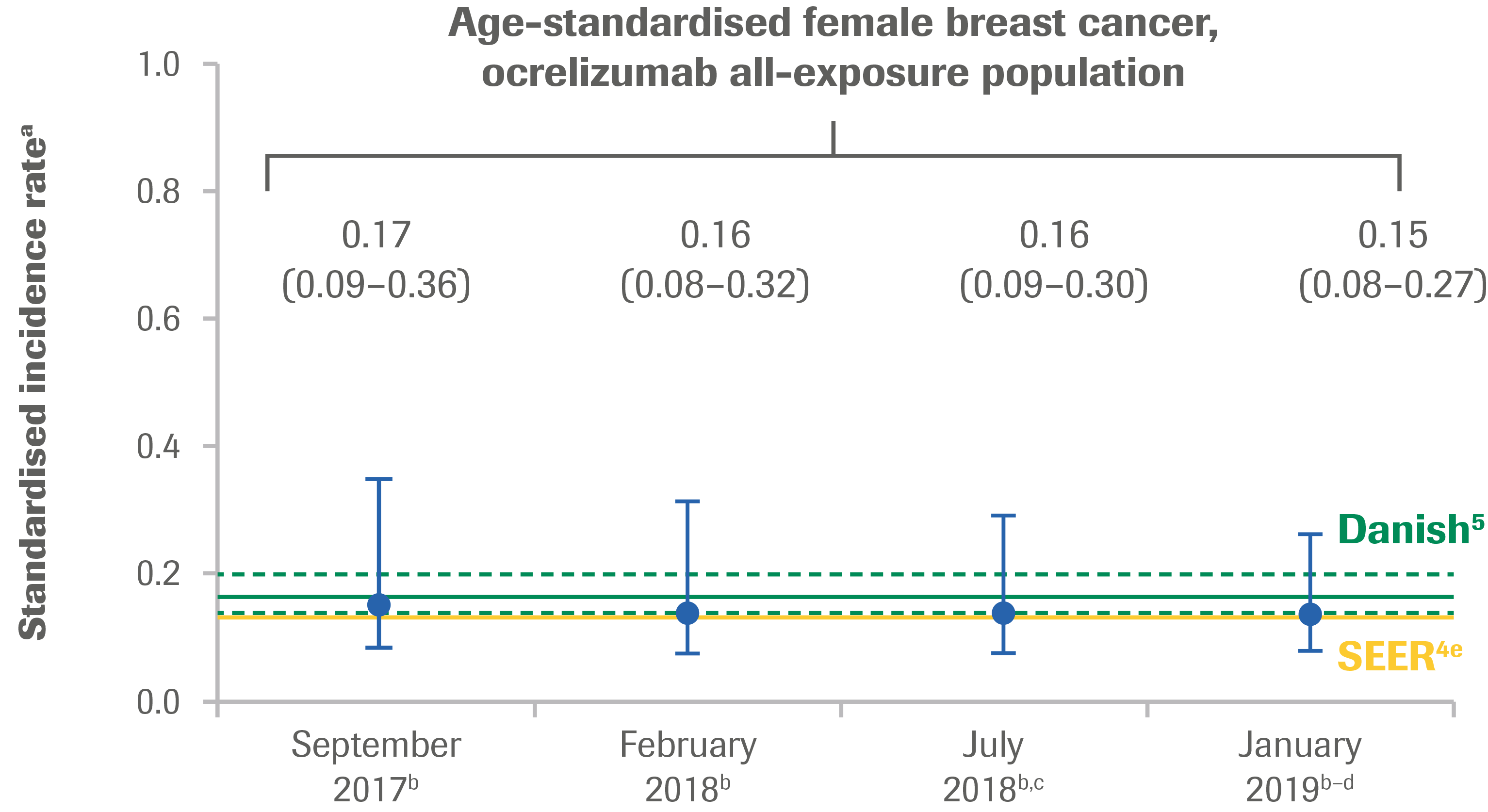
a The incidence rate of first malignancy (number of first malignancy events per 100 PY, excluding NMSC) was calculated. Standardised incidence rates are presented using “age at event onset” (age range: 15–64 years). Standardised incidence rate (95% CI) for all malignancies: SEER: 0.31 (0.30–0.31); Danish MS registry: 0.30 (0.27–0.35); for female breast cancer: SEER: 0.14 (0.14–0.14); Danish MS registry: 0.17 (0.14–0.21).
b Includes patients who received any dose of OCR during the controlled treatment and associated OLE periods of the Phase II and Phase III studies, plus VELOCE, CHORDS, CASTING and OBOE.
c Also includes patients who received any dose of OCR during ENSEMBLE.
d Also includes patients who received any dose of OCR during the LTE associated with CASTING.
e NMSC is not reported in SEER.
Table 1: Yearly Incidence Rates of all Malignancies (A) and Female Breast Cancer (B) in the Ocrelizumab All-Exposure Populationa
| A. All Malignancies | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| All-Exposure Population | PY | No. of AEs | AEs per 100 PY (95% CI) |
| Year 1 (N=4,611) | 4,357 | 12 | 0.28 (0.14–0.48) |
| Year 2 (N=3,870) | 3,290 | 15 | 0.46 (0.26–0.75) |
| Year 3 (N=2,234) | 2,048 | 14 | 0.68 (0.37–1.15) |
| Year 4 (N=1,835) | 1,696 | 10 | 0.59 (0.28–1.08) |
| Year 5 (N=1,542) | 1,267 | 7 | 0.55 (0.22–1.14) |
| Year 6 (N=1,106) | 991 | 6 | 0.61 (0.22–1.32) |
| B. Female Breast Cancer | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| All-Exposure Population | PY | No. of AEs | AEs per 100 PY (95% CI) |
| Year 1 (N=2,939) | 2,782 | 1 | 0.04 (0–0.20) |
| Year 2 (N=2,474) | 2,078 | 7 | 0.34 (0.14–0.69) |
| Year 3 (N=1,369) | 1,241 | 5 | 0.40 (0.13–0.94) |
| Year 4 (N=1,106) | 1,021 | 2 | 0.20 (0.02–0.71) |
| Year 5 (N=921) | 749 | 1 | 0.13 (0–0.74) |
| Year 6 (N=643) | 575 | 0 | 0 (0–0.64) |
- The incidence rates of malignancies are derived from varied sources, and intended to provide context. Confounding factors that may influence incidence rates have not been accounted for, and therefore, no direct comparisons should be made. Such factors may include, but are not limited to: type of MS, disease duration, risk factors, geographical region, population size, drug exposure, comorbid conditions, treatment history, and duration of follow-up
Post-Marketing Experience6
- As of 31 July 2019, 76,554 female patients with RMS and PPMS had started ocrelizumab globally outside of clinical trials,† corresponding to an exposure of 74,039 PY
- A total of 95 cases reporting breast cancer were received, resulting in a crude incidence rate (95% CI) of 0.128 (0.105–0.160)
Prescribing information
Indications vary in different countries. The local prescribing information from your country is the primary source of information on the known and potential risks associated with ocrelizumab.
*NMSC data have been excluded from these analyses as they are classified as a non-serious event and excluded from databases like SEER. †There are well-recognised limitations that should be considered when interpreting spontaneous post-marketing safety reports, including events may not be causally related to drug exposure; in the real-world setting, events are frequently confounded by factors such as multiple drug use and the presence of pre-existing comorbidities; reporting bias may exist for more significant outcomes, which may result in an overrepresentation of the more serious outcomes; and reporting rates can be stimulated by external factors such as press reports.
The causes of malignancies are recorded as reported to the company; while the company follows up on all reports to identify the cause, an exact diagnosis is not always possible. Some of the investigations remain ongoing and, therefore, the information may be subject to change.
AE, adverse event; CI, confidence interval; IFN, interferon; LTE, long-term extension; MS, multiple sclerosis; NMSC, non-melanoma skin cancer; OCR, ocrelizumab; OLE, open-label extension; PY, patient-years; SEER, Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results Program.
- Hauser SL, et al. N Engl J Med 2017;376:221–234;
- Montalban X, et al. N Engl J Med 2017;376:210–220;
- Hauser SL, et al. Presented at ECTRIMS 2019 (P648);
- Nørgaard M, et al. Mult Scler Relat Disord 2019;28:81–85;
- SEER. https://seer.cancer.gov/about/overview.html. Accessed 14 February 2019;
- Roche data on file